by Teanna Anthony
All about animals

Zoology is the scientific stud of the behavior, structure, physiology, classification and distribution of animals. All living things have specific characteristics of life that make them who they are.
Characteristics of life:
-
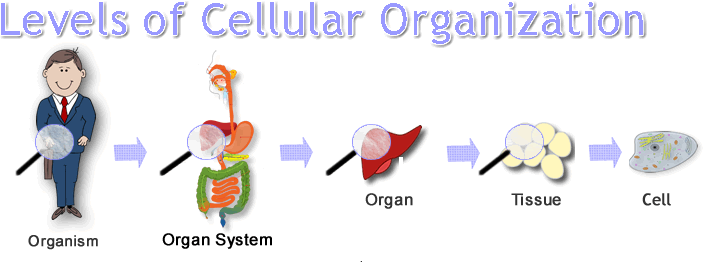
cellular organization
-
reproduction
-
metabolism
-
homeostasis
-
response to stimuli
-
heredity
-
growth and development
-
adaptation through evolution
All living systems have cellular organization and chemical uniqueness in much they are made up of large Macromolecules. Macromolecules are divided into four categories:
-
Nucleic Acid
-
Proteins
-
Carbohydrates
-
Lipids
These macromolecules are organized in a complex hierarchy that builds on previous levels.Within each level in this hierarchy organization, there are unique characteristics that appear at a given level of organization.
Along with cellular organization, all living things have the ability to reproduce. There are two types of reproduction, asexually and sexually. Asexual reproduction a type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single organism, and inherit the genes of that parent only. Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which the production of new living organisms by combining genetic information from two individuals of different types (sexes). In most higher organisms, one sex (male) produces a small motile gamete that travels to fuse with a larger stationary gamete produced by the other (female).
Considering that all living organisms are made up of cells, all living organisms must have a genetic program that has information that is contained in genes that specifically encode DNA and must be able to successfully transmit traits through heredity. Within these cells, there are a series of complex processes that occur to provide the cell with energy which is metabolism. There are two types of metabolism: catabolic and anabolic. Catabolism is metabolic pathways that breaks down molecules into smaller units that are either oxidized to release energy, or used in other anabolic reactions. Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules in living organisms from simpler ones together with the storage of energy; constructive metabolism. All of these processes work cohesively to ensure that the cells within the organisms body maintains homeostasis and works properly.
Over the lifespan of an organism, the organisms go through a change called metamorphism, which occurs during the post embryonic period of their development. These changes allow the organisms to adapt to the environment around them and evolve overtime. Charles Darwin, a geologist, naturalist, and biologist, developed a theory of evolution to explain how organisms adapt and evolve over time.
Darwins Theory of Evolution proposes that all life is related and has descended from a common ancestor. Darwin's theory of evolution exclaims that creatures evolve from more simplistic ancestors naturally over time through descent modification. This means that as random genetic mutations occur within an organism's genetic code within their cells, the beneficial mutations aid in the survival of these organisms and are passed on to the next generation. Over time, these helpful mutations accumulate and the result is an entirely different organism or creature.
Darwin's theory of evolution brought about the many different ways that organisms are grouped together and classified today.